The Regional E-waste Monitor for the Arab States 2021
The Regional E-waste Monitor for the Arab States 2021 provides an assessment of statistics, legislation, and management infrastructure of e-waste in Algeria, Bahrain, Comoros, Djibouti, Egypt, Iraq, Jordan, Kuwait, Lebanon, Libya, Mauritania, Morocco, Oman, The State of Palestine, Qatar, Saudi Arabia, Somalia, Sudan, Syrian Arab Republic, Tunisia, the United Arab Emirates and Yemen. The e waste generation in the region increased by 61 per cent from 1.8 Mt (4.9 kg/inh) in 2010 to 2.8 Mt (6.6 kg/inh) in 2019. The largest e-waste generator is Saudi Arabia, with 595 kilotons (kt) (or 13.2 kg/inh) of e-waste, while the lowest is Comoros (0.6 kt, or 0.7 kg/inh), which reflects the vast diversity of the region. The Arab States collected and managed a total of 2.2 kt (0.01 kg/inh) of e-waste in 2019, which equates to a collection rate of 0.1 per cent. This takes place in Jordan, the State of Palestine, Qatar and the United Arab Emirates. Egypt has seven licensed treatment facilities for e-waste, but it was unable to provide official data on the amount of e-waste collected and managed. No specific e-waste legislation is in place in any State in the region.
The 2050 Electronic and Electrical Waste Outlook in West Asia provides projections for Bahrain, Iraq, Jordan, Kuwait, Lebanon, Oman, State of Palestine, Qatar, Saudi Arabia, Syrian Arab Republic, United Arab Emirates, and Yemen – 99.9% of electrical and electronic waste equipment (e-waste) is currently unmanaged or mismanaged. The future of e-waste management in West Asia is assessed for two contrasting scenarios. The Business as Usual scenario represents present-day consumption, lifespans, and recycling behaviours, extrapolated to 2050. Alternatively, the Circular Economy scenario assumes that products become more durable, are shared and reused more, and are managed in an environmentally sound manner when becoming e-waste. A transition toward a circular economy approach will have positive impacts on both the reduction of 33 per cent electronic and electrical equipment placed on the market, 14 per cent less e-waste generation and an estimated total of 130 t of gold, 5 t of rare earth metals, 17 Mt of iron and steel, and many other materials could be recycled between 2020 and 2050. Simultaneously, a larger proportion of hazardous materials and greenhouse gases will be managed in an environmentally sound manner, leading to mitigated emissions of up to 6 t of mercury, 60 t of cadmium, and 53 Mt CO2-eq. It is estimated that roughly 225,000 full-time equivalent jobs would be created for repair of used EEE and collection and pre-treatment of e-waste.

Monitor Features
1. What is E-waste?
Definition, product categories, disposal routes, key issues
4. Statistics
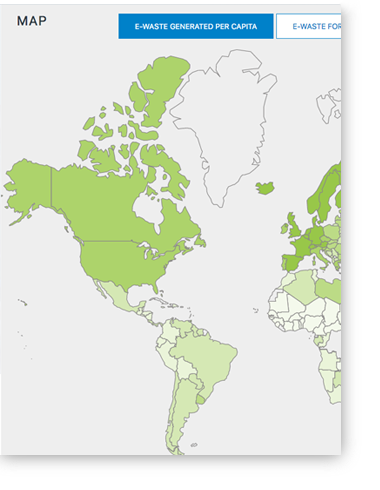
EEE POM and E-waste Generated, Categories, ESM
7. Common Issues
Five Driving Reasons
2. Methodology
Statistics, Management Assessment,
Sources
5. Transboundary Movement
Policies, Quantities, Issues and Impacts
8. Recommendations
3. Regional Overview Legislation and Systems
Status, International Agreements, Stakeholders, Projects
6. Management Assessment
Comparative Performance Review
9. Country Profiles
Book Preview
About the authors

Giulia Iattoni
Giulia Iattoni is a programme associate at UNU-ViE SCYCLE. Giulia graduated cum laude in environmental engineering at the University of Bologna and spent a research period at the Technical University of Vienna, where she focused on water quality and resource sustainability. Since 2019, Giulia has been involved on various projects on e-waste data collection and quantification, in addition to projects concerning the analysis of e-waste management models and related environmental impacts at national and regional levels. She designs and conducts workshops to build institutional capacity on e-waste statistics and legislation for several countries worldwide.

Elise Vermeersch
Elise Vermeersch is a research associate at UNU-ViE SCYCLE. She is working on several projects related to the management and monitoring of waste and chemicals, sustainable development and the circular economy. She is particularly interested in initiatives that deal with the illegal transboundary movement of waste. Elise started working for the United Nations in 2013 in the fields of crime prevention and criminal justice. She graduated in law and holds a double master’s degree in new technologies law from the University of Lille and the University of Murcia.

Dr. Innocent Nnorom
Dr. Innocent Nnorom works at Abia State University in Nigeria. He received his PhD in Analytical/Environmental Chemistry from the University of Ibadan, having studied pollution from e-waste management in Southern Nigeria. He was part of the 2009 E-waste Summer School. He has participated in several e-waste projects, including the E-waste Africa Project and the Person in Port (PiP) Project. He is a Senior Research Fellow at the Basel Convention Coordinating Centre for Africa (BCCC-A) in Nigeria. In 2019, he was a Visiting Research Fellow at the University of Manchester. He has contributed to the Global E-waste Monitor in recent years.

Dr. Cornelis Peter Baldé (Kees)
Dr. Cornelis Peter BALDÉ (Kees) is a Senior Programme Officer at the Sustainable Cycles Programme at the United Nations University. At the UNU, Kees’s main tasks are to lead the statistical work, build institutional capacity on waste statistics in various countries, and waste policies, provide policy advice on e-waste to countries, and supervise staff and the strategic development of the team. He is one of the founders of the Global E-waste Statistics Partnership. Kees is currently the co-chair of the Taskforce on Waste Statistics of the UNECE Conference of European Statisticians that is tasked with developing a framework for waste statistics that is sufficient for monitoring current and future circular economy policies as well as waste policies. Additionally, Kees has been selected by the Dutch government as a member of the board of directors of the Dutch Waste Electronical and Electronic Appliances Register, a role he has held since 2015. In 2018, the Global E-waste Monitor 2017 won the European Advanced SDG award from the Diplomatic Academy in Vienna. At Statistics Netherlands, Kees received the Innovation Award for the Dutch Green Growth publication in 2012. Previously, Kees worked at Statistics Netherlands as the deputy head of the Environment Statistics team. He earned his PhD on hydrogen storage at the Faculty of Chemistry at Utrecht University.

Dr. Ruediger Kuehr
Dr. Ruediger Kuehr is the Director of UNU’s Sustainable Cycles (SCYCLE) Programme and Head of the recently established UNITAR Bonn Oÿce. He also serves as Head and Senior Manager of the SCYCLE Programme under UNITAR. As a political and social scientist by education, Ruediger has worked for more than twenty years on the e-waste challenge. He co-founded the StEP Initiative, co-initiated the development of an e-waste coalition among the various UN organisations and the SCYCLE Programme, and initiated the permanent E-waste Academies and E-waste Monitors at the global, regional, and national levels. But the foundation of Ruediger’s work is in establishing strategic approaches to sustainability, which renders life-cycle thinking indispensable in his activities; as such, he is also a frequent speaker for forward-thinking at conferences and in media appearances.
Other E-waste Data Resources
Regional E-waste Monitor Asia 2016
• Regional E-waste Monitor 2016: East and Southeast Asia